2023 has quietly ended. In this year, almost all of us have suffered from COVID-19, and at the same time, we have deeply realized the importance of physical health. Physical examination is becoming increasingly important in our hearts. Do you know how various indicators are measured?
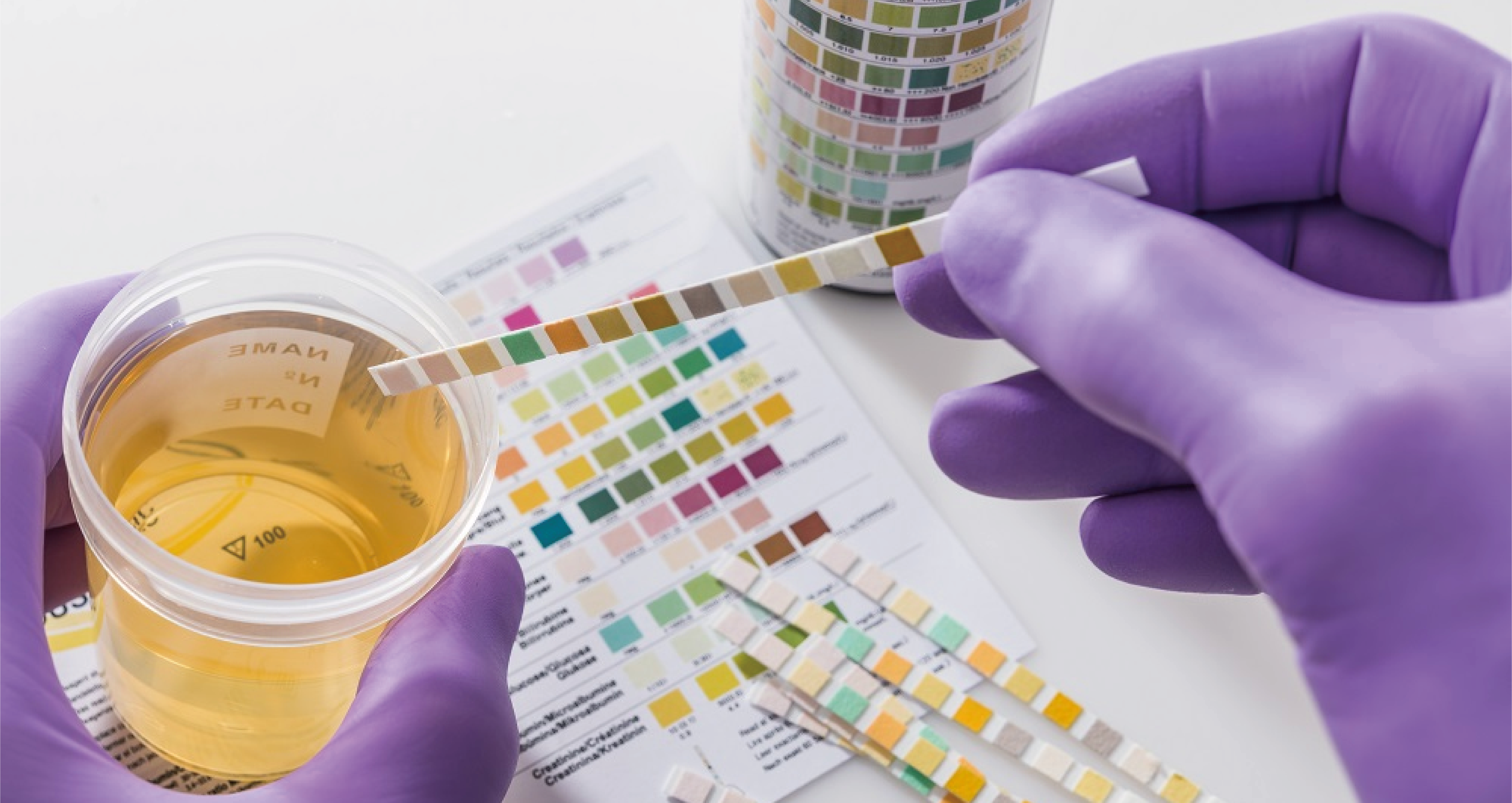
Today we will introduce one of the commonly used detection methods, dry chemistry/dry biochemistry, which is commonly used to measure liver function, kidney function, electrolytes, blood sugar, blood lipids, uric acid and other indicators. In addition to being used in physical examination items, dry chemistry test strips are also widely used in grassroots hospitals, blood stations, and animal hospitals.
Dry biochemistry/dry chemistry belongs to the category of bedside detection (POCT) and has many advantages of POCT, such as fast time, low threshold, rich detection items, and low cost. These advantages make dry chemistry test strips very suitable for physical examinations and community hospital examinations, which coincides with the graded diagnosis and treatment policy vigorously promoted by the country to increase the proportion of grassroots diagnosis and treatment. Therefore, compared to the fiercely competitive lateral chromatography test, traditional biochemical detection reaction substrates are liquid, while dry chemistry uses solid-phase reagent technology to solidify the chemical reagents onto the carrier. When the liquid sample is added, the solidified reagents will dissolve and react with the tested components in the sample, showing a certain color and causing scattering phenomenon. The detector captures and reads the reflected light, establishing the relationship between reflectivity and the concentration of the tested substance, So as to conduct qualitative or quantitative analysis. Dry chemistry can be roughly divided into two categories based on structure: single-layer drying and multi-layer drying. As the name suggests, single-layer drying refers to only having a single-layer reaction membrane, such as urine test strips. Multi layer drying generally has multiple membrane materials before and after the reaction membrane, such as blood lipid test strips. The function of various membrane materials is to remove interfering substances from the sample, commonly seen as adding a blood filtration membrane to remove color interference from red blood cells. Paper, dry chemical test paper, may be a huge potential market. Now let’s delve deeper into dry chemistry!
The characteristics of dry biochemistry include: fast reaction, usually 1-5 minutes; Easy to operate, no need for pre-treatment, simple reagent storage, and easy equipment maintenance; The samples are diverse and consume less, and the sample types can be whole blood, serum, plasma, urine, cerebrospinal fluid, etc. The sample loading volume is generally 5-20uL.
In addition to chemical reagents, the most important component of dry chemistry is the membrane material. The membrane material is the place where the reagents are fixed, as well as the carrier for eliminating interference and color reading. The membrane material commonly used for single-layer drying is cotton fiber, and the key parameters are:
1. Absorption consistency: In large-scale production, the inert absorption of chemical substances by cotton fibers ensures the consistency of different test strips;
2. Mechanical strength: As a reaction carrier, the membrane material needs to go through a process of wetting, drying, and then wetting. If the mechanical strength is unqualified, it is easy to cause fracture, which affects the reading results.
Post time: Jan-16-2024