Chylosis blood mainly has the following effects on blood routine, biochemistry, and coagulation function testing:
1. Blood routine
Milk blood contains a large amount of chyle particles, which the instrument may misread as substances such as blood cells. Therefore, “milk blood” specimens may exhibit significant increases in hemoglobin (HGB), platelets (PLT), and white blood cells (WBC).
The hemoglobin detection uses colorimetric method, and the increase in turbidity of “milk blood” greatly interferes with its detection, leading to a false increase in hemoglobin, which in turn affects the mean corpuscular hemoglobin content (MCH) and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC), resulting in
2. Biochemical indicators
Chylose particles can scatter light, causing significant interference to commonly used colorimetric or turbidimetric methods in biochemical testing, and interference errors are positively correlated with sample turbidity, affecting the accuracy of test results. When measuring total bilirubin (TBIL), chylomicrons increase absorbance, leading to higher TBIL results.
The turbid lipid also has some interference with the endpoint method, but the influence of chyle blood on dry chemistry, enzyme method, rate method, etc. is not significant.
At present, literature reports that “milk blood” has varying degrees of impact on indicators such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), total protein (TP), albumin (ALB), calcium (Ca), phosphorus (P), magnesium (Mg), total bilirubin (TBIL), direct bilirubin (DBIL), creatinine (CREA), and homocysteine (HCY), leading to abnormally high or even impossible results.
3. Coagulation function
There are a large number of fat particles in plasma, and the turbidity of chyle can interfere with the measurement system, which may prolong the plasma prothrombin time (PT) and shorten the activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT).
The degree of plasma chyle has a significant impact on the activity of coagulation factor VIII (F VIII: C) and fibrinogen (Fg), and the recovery rates of F VIII: C and Fg in moderate and severe chyle blood are significantly reduced.
The specific operations for eliminating “milk blood” in blood routine, biochemistry, and coagulation function testing are as follows:
The blood routine samples are directly tested on the computer, and it is not easy to detect lipid turbidity before testing. However, the instrument can indicate “turbidity/HGB interference” and abnormally increased HGB, MCH, and MCHC to attract attention. After centrifugation of chyle blood, it is clear at a glance and is usually corrected for hemoglobin using plasma exchange and formula correction methods.
Plasma exchange
After centrifugation, the upper layer of plasma is aspirated and an equal amount of physiological saline is added. After thorough mixing, it is tested on the machine. The plasma exchange method is relatively cumbersome, and the WBC and PLT layers at the bottom of the plasma are easily lost. Therefore, HGB, MCH, and MCHC can use the results of the exchange, while other parameters of the blood routine use the original results.
Formula correction method
Suck out the upper layer of plasma after centrifugation, measure the obtained plasma, and apply the correction formula for calculation.
HGB correction value=before HGB correction – (HGB chyle plasma – HGB chyle plasma) × Before HCT correction)
MCH correction value=HGB correction value/before RBC correction, MCHC correction value=HGB correction value/before HGT correction
The HGB, MCH, and MCHC results obtained by the correction method are basically consistent with those obtained by the substitution method, which is easy to operate, but the formulas are complex and the computational workload is large.
Based on the interference mechanism of chyle blood, methods to eliminate the interference of chyle blood on biochemical and coagulation detection include physical and chemical methods. The former includes serum dilution method, physiological saline dilution method, high-speed centrifugation method, and low-temperature refrigeration method, while the latter includes polyethylene glycol (PEG) method, ether extraction method, lipid scavenger method, high-performance liquid chromatography method, and dry chemistry method.
When dealing with chyle blood, some biochemical items can also be replaced with detection methods with different principles, but biochemical detection methods using colorimetric and turbidimetric principles still dominate. High speed centrifugation is commonly used in clinical practice to eliminate the interference of chyle particles.
The high-speed centrifugation method is set at a centrifugation speed of 13000-14000r/min, centrifugation for 15-20min, and the lower clear liquid of the sample is taken after centrifugation for the detection of various clinical biochemical and coagulation indicators. The use of high-speed centrifugation method is very effective in eliminating interference from chylomyosis, and both proportional error and constant error are greatly reduced. However, the triglycerides (TG) and total cholesterol (TC) in the lower clear liquid after centrifugation decrease, especially the TG level will significantly decrease, so this method is not suitable for detecting TG or TC.
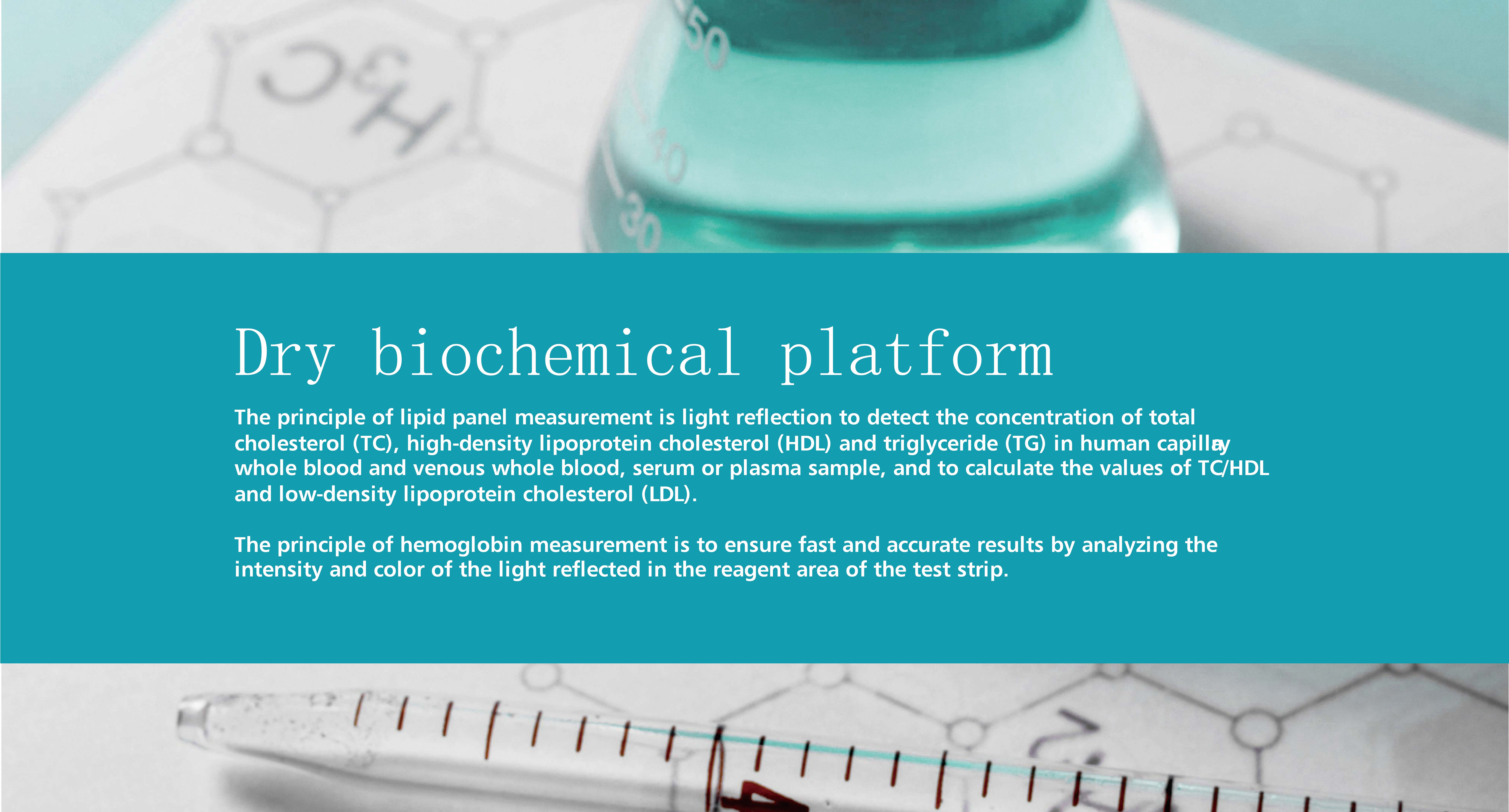
blood glucose monitoring system, lipid panel monitoring system, hemoglobin monitoring system, uric acid monitoring system, uric acid monitoring system, SARS-CoV-2 rapid test, Infectious disease test kits, women healthcare test
Post time: Feb-04-2024